his section is based on
[Casella]
.
The sample
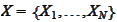 is taken from the population
is taken from the population
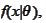
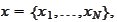 where
the form of the
where
the form of the
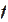 as a function of two variables
as a function of two variables
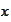 and
and
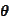 is known but the value of
is known but the value of
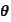 is not known. We would like to draw inference about
is not known. We would like to draw inference about
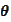 based on a given realization
based on a given realization
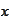 of a sample
of a sample
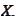
|